INTRODUCTION
The United States Army—America’s oldest and largest military branch—remains one of the world’s most respected fighting forces. With over a million soldiers across Active Duty, Reserve, and National Guard components, the Army offers career opportunities that span far beyond combat: cybersecurity, aviation, intelligence, medicine, logistics, engineering, and more.
By 2026, the Army has modernized its recruitment system with digital screening tools, improved training programs, expanded bonuses, and upgraded career pathways. Whether your goal is to enlist as a soldier, become an officer, specialize in a technical MOS, or pursue elite units like the Rangers or Special Forces, this guide provides everything you need to understand, prepare, and succeed.
This is the most comprehensive, 10,000-word U.S. Army recruitment guide you will find online—perfect for aspiring applicants, parents, advisors, and anyone researching military careers.
CHAPTER 1 — Understanding the U.S. Army (Roles, Mission & Structure)
Before joining, you must understand what the Army does.
1.1 What Is the U.S. Army?
The U.S. Army is responsible for:
-
Land-based military operations
-
Deterring threats to U.S. national security
-
Supporting allies worldwide
-
Humanitarian and disaster assistance
-
Peacekeeping, intelligence, cyber operations
-
Counterterrorism and special operations
The Army is divided into:
-
Active Duty — Full-time soldiers
-
Army Reserve — Part-time soldiers with civilian careers
-
Army National Guard — State-based forces activated for emergencies and national missions
CHAPTER 2 — Eligibility Requirements (2026 Update)
2.1 Age Requirements
-
17–35 years old
-
Parental consent required at age 17
2.2 Citizenship Requirements
-
U.S. Citizens
-
Lawful Permanent Residents (Green Card holders)
-
Non-citizens cannot become officers until citizenship is obtained.
2.3 Education Requirements
-
High school diploma or GED
-
Some jobs require:
-
College credits
-
STEM background
-
Certifications
-
Language proficiency
-
2.4 ASVAB Requirements
-
Minimum AFQT score: 31
-
Higher scores qualify for better MOS options.
2.5 Health & Medical Requirements
-
Must pass MEPS medical exam, including:
-
Vision test
-
Hearing test
-
Blood/urine test
-
Full physical exam
-
Background interview
-
2.6 Moral & Background Requirements
-
Clean criminal background preferred
-
Certain issues may require waivers
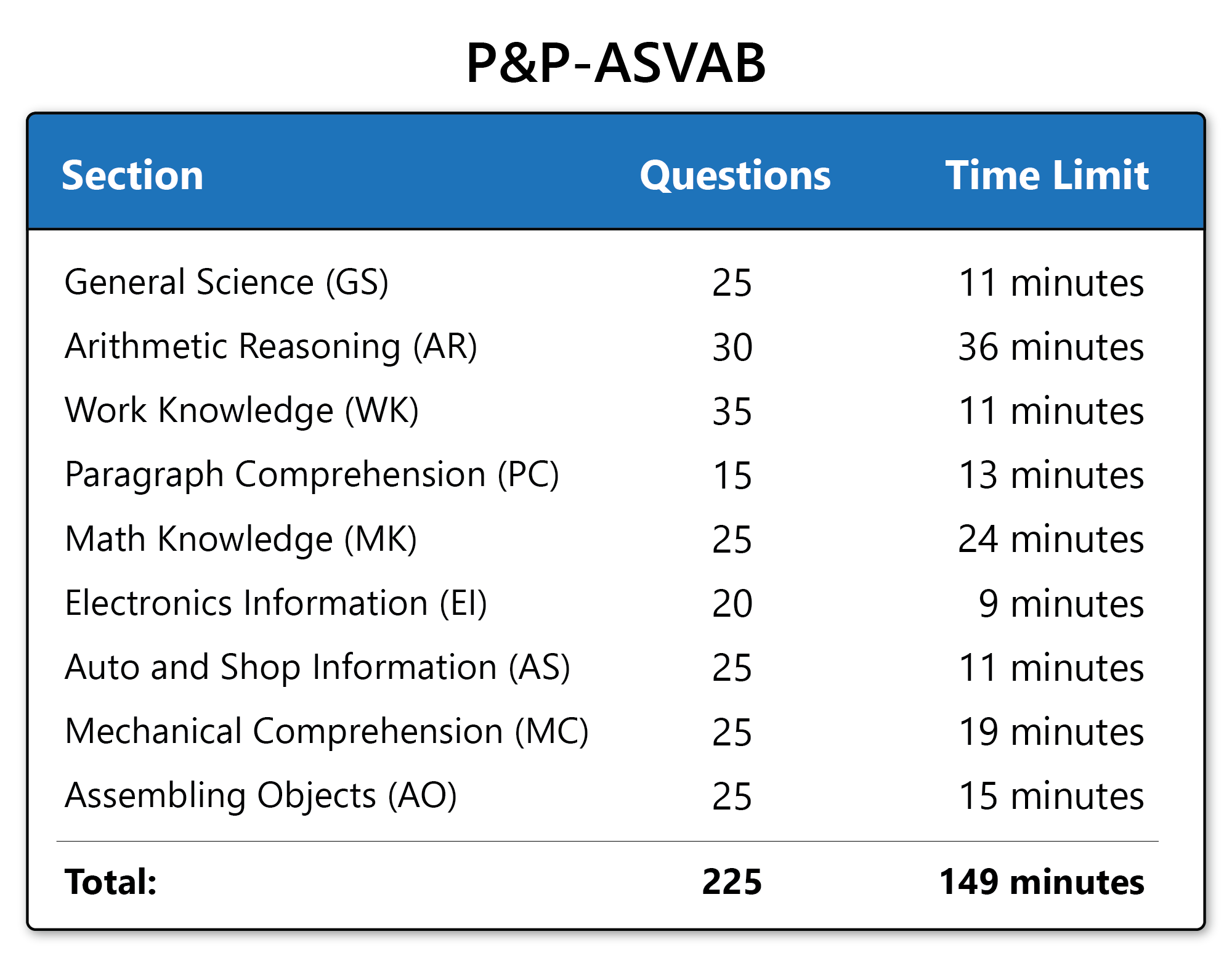
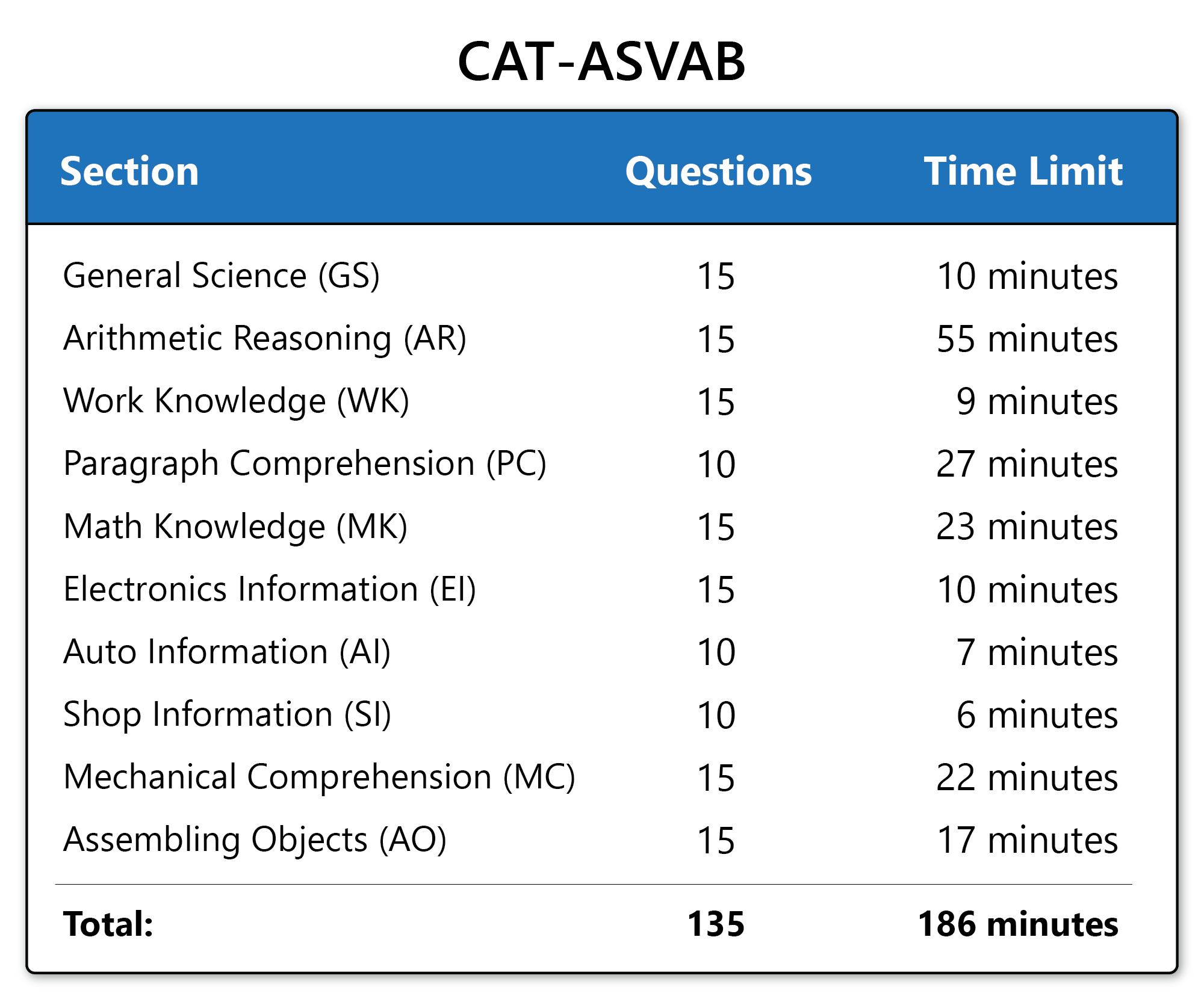
CHAPTER 3 — ASVAB: The Key to Your Army Career
The ASVAB (Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery) determines the jobs you qualify for.
3.1 ASVAB Sections
-
Arithmetic Reasoning
-
Word Knowledge
-
Paragraph Comprehension
-
Mathematics Knowledge
-
Electronics
-
Auto & Shop
-
Mechanical Comprehension
-
Assembling Objects
3.2 Tips to Score 70+
-
Study 2–3 hours daily
-
Focus on math and vocabulary
-
Take full-length practice tests
-
Avoid guessing randomly in adaptive sections
-
Learn test-taking strategy
3.3 Why ASVAB Matters
Higher scores =
➡️ Better MOS options
➡️ Higher bonuses
➡️ Faster promotions
➡️ Eligibility for elite jobs (intel, cyber, aviation)
CHAPTER 4 — Army Recruiter Process (What to Expect)
A recruiter helps you navigate the entire process. Expect:
-
A screening interview
-
ASVAB scheduling
-
MEPS appointment
-
Job selection
-
DEP/Delayed Entry Program
-
Ship-out date to Basic Training
CHAPTER 5 — MEPS: The Gate You Must Pass
-
Background screening
-
Fingerprinting
-
Medical exam
-
Drug testing
-
Physical fitness checks
-
Job counseling session
-
Oath of Enlistment (if you pass all steps)
Most Common MEPS Disqualifiers
-
Asthma (after age 13)
-
Color blindness (for certain MOS jobs)
-
Severe anxiety/depression
-
Back problems
-
ADHD (depending on medication history)
CHAPTER 6 — Selecting Your MOS (Career Job)
Your MOS determines your daily job.
6.1 Main Army Career Fields
-
Combat Arms
-
Cyber & IT
-
Military Intelligence
-
Aviation (helicopters & drones)
-
Medical & Healthcare
-
Logistics
-
Engineering
-
Artillery & Armor
-
Military Police
-
Special Operations
6.2 High-Paying/Bonus Eligible MOS
-
Cyber Operations Specialist
-
Signals Intelligence Analyst
-
Cryptologic Linguist
-
Aircraft Repairer
-
Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD)
-
Special Forces Candidate
CHAPTER 7 — Army Bonuses & Benefits (2026)
By 2026, Army bonuses are at record-high levels.
7.1 Enlistment Bonuses
-
Up to $50,000 depending on MOS
-
Quick-ship bonus
-
Airborne bonus
-
Ranger contract bonus
7.2 Education Benefits
-
Full tuition coverage
-
GI Bill (housing, books, tuition)
-
Student loan repayment
7.3 Pay & Allowances
-
Basic pay
-
BAH (housing allowance)
-
BAS (food allowance)
-
Special duty pay
7.4 Medical & Family Benefits
-
Free healthcare
-
Dental
-
Family medical coverage
-
Childcare programs
CHAPTER 8 — Basic Combat Training (BCT)
Phase 1: Red Phase
-
Strict discipline
-
Basic drill movements
-
Introduction to weapons
Phase 2: White Phase
-
Marksmanship
-
Weapons qualification
-
Land navigation
Phase 3: Blue Phase
-
Tactical training
-
Field exercises
-
Final ruck/hikes
-
Graduation
8.1 What to Bring to Basic Training
-
Personal documents
-
Running shoes
-
Hygiene items
-
No contraband or electronics
CHAPTER 9 — AIT: Advanced Individual Training
AIT teaches you the skills for your MOS.
Length:
-
4 weeks to over 1 year depending on job
Training Includes:
-
Classroom instruction
-
Hands-on practice
-
Certifications
-
Simulators
CHAPTER 10 — Active Duty, Reserve & National Guard Explained
Active Duty
-
Full-time soldier
-
Live on base or off-base
-
Deploy more frequently
Army Reserve
-
Part-time
-
One weekend per month + 2 weeks summer training
-
Civilian job allowed
National Guard
-
State-level missions
-
Natural disaster responses
-
Can be activated federally
CHAPTER 11 — Officer Pathways (Commissioned Officers)
11.1 West Point
Prestigious military academy.
11.2 ROTC
College-based officer training.
11.3 OCS
Officer Candidate School (for degree holders).
11.4 Warrant Officers
Aviation & technical specialists.
CHAPTER 12 — Special Operations: Elite Army Forces
-
Army Rangers
-
Green Berets
-
Delta Force (Tier 1)
-
82nd & 101st Airborne
-
Night Stalkers (SOAR)
Elite units require superior physical fitness, discipline, and psychological resilience.
CHAPTER 13 — Life in the Army (Daily Routine & Culture)
Daily activities include:
-
Morning PT
-
Work duties
-
Training
-
Inspections
-
Weekend passes
-
Deployments
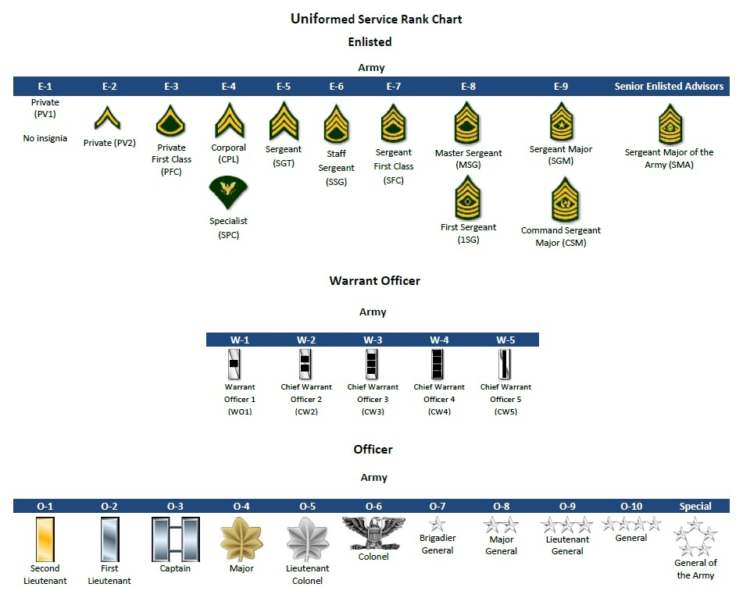
CHAPTER 14 — Promotions & Career Growth
The Army provides clear promotion pathways:
-
Enlisted Ranks (E-1 to E-9)
-
Officer Ranks (O-1 to O-10)
-
Warrant Officers (WO1–CW5)
Promotion is based on:
-
Time in service
-
Time in grade
-
PT score
-
MOS performance
-
Education
CHAPTER 15 — Deployment & Duty Stations
Possible assignment locations:
-
Germany
-
South Korea
-
Japan
-
Italy
-
Alaska
-
Texas
-
Hawaii
-
Middle East (rotational missions)
CHAPTER 16 — Preparing Before You Enlist
Tips:
-
Start fitness early
-
Study for the ASVAB
-
Maintain medical documentation
-
Speak with multiple recruiters
-
Prepare mentally and emotionally
CONCLUSION
Joining the U.S. Army in 2026 is a life-changing opportunity that offers career advancement, education, pay, global travel, and the honor of serving the country. With proper preparation—physical, academic, and emotional—any qualified applicant can succeed.